ABOUT GRESB
GRESB (http://gresb.com/), the Global ESG Benchmark for Real Assets, is an annual benchmarking assessment to measure the ESG integration of owners and asset managers for real assets (real estate and infrastructure) and funds. Founded in 2009 by a group of European institutional investors who were instrumental in launching Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI), it is now employed worldwide. GRESB is composed of two organizations, GRESB Foundation, where GRESB Standards are developed and managed and GRESB B.V., which offers various services, in order to separate functions and enhance organizational transparency.
Currently, there are about 150 "Investor Members" using GRESB data to form their investment strategies and shape engagement with investees. In Japan, more than 10 institutions are members, and they are utilizing GRESB data to promote ESG in the real asset sector (as of Oct 2025).
There are also "Industry Supporters" such as ARES (Association for Real Estate Securitization), which further promote GRESB in the market. Leading among these is CSR Design Green Investment Advisory, Co., Ltd., which has been officially promoting GRESB in the Japanese market since 2011, and is granted as the Premier Partner for Japan.
GRESB are conducted every year from April through July, with results published in October. Detailed results are available for "GRESB Investor Members." These GRESB Assessments serve as a reporting tool for real estate/infrastructure companies and funds as well as a monitoring tool of their ESG performance.
Should you need information on the ESG initiatives of real estate and infrastructure companies and funds, and/or need to confirm the level of your own ESG initiatives on a global basis, taking part in a GRESB Assessment is your first step. For those wishing to incorporate ESG related information into their investment and financing strategies, becoming an Investor Member is an effective option.
GRESB Assessments
GRESB Assessments can be broadly divided into two categories: GRESB Real Estate, which evaluates efforts in standing investments and the development of new construction and major renovation projects, and GRESB Infrastructure, which evaluates efforts in infrastructure funds and assets. GRESB Real Estate is subject to GRESB Public Disclosure Assessment, which measures the quality of information disclosure.



GRESB Real Estate
Inaugurated in 2009, the 16th annual assessment was conducted in 2025. Although other green building certifications such as CASBEE (Japan), LEED (US) and BREEAM (UK) have been developed, GRESB is virtually the only benchmarking tool of company or fund level sustainability performance in the real estate sector.
Several agencies provide ESG assessments or ratings of issuers. That being said, GRESB is regarded as the de-facto standard in the real estate sector and has earned its place as a global standard. It aligns with various other global frameworks such as PRI and SASB, as well as PCAF which is the global GHG accounting standard for financed emissions, and CRREM which is an analysis tool for climate change transition risks in the real estate sector. Because its investors are actively committed, it focuses on material issues and can be used for due diligence and the monitoring of real estate investments by institutional investors.
Real Estate Assessment
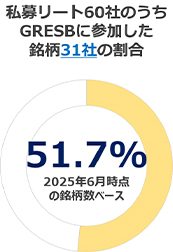
In 2025, 2,382 entities participated in GRESB Real Estate Assessment globally of which Japan provided 142 (62 listed entities including 56 J-REITs, and 80 private entities from 52 companies). It is noteworthy that an even higher number of J-REITs (99.7% based on market cap. as of 29 September 2025) participated in the 2025 Assessment. This puts Japan in third place globally for number of participants, following the United States and the United Kingdom.
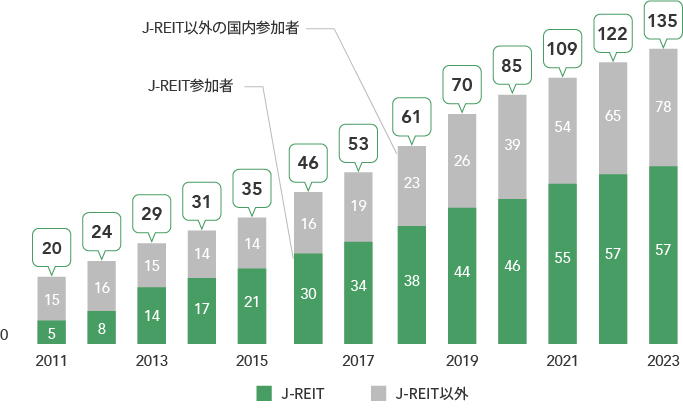
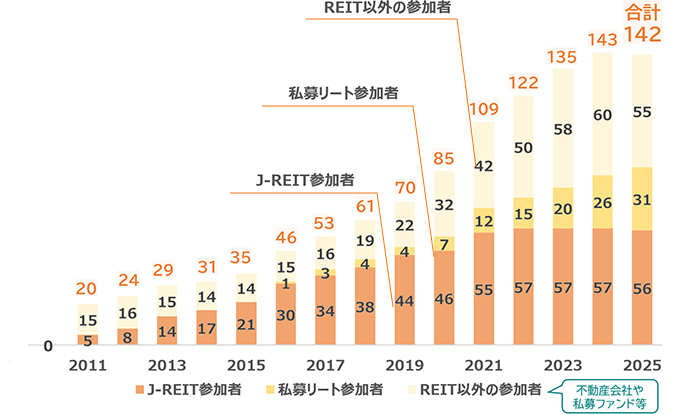
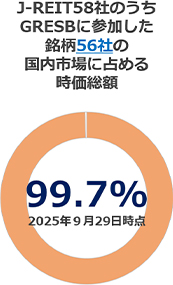
The GRESB Real Estate Assessment offers two benchmarks, namely the "Standing Investment Benchmark," which assesses commercial real estate operation, and the "Development Benchmark," which focuses on new development and major renovation projects. Both are evaluated according to the 5-star rated “GRESB Rating,” where “5 Stars” is the highest rank for participants in the top quintile based on the global ranking of GRESB Overall Score.
In addition, GRESB has introduced a Residential Component as a benchmarking tool for residential assets in the 2025 assessment. Participants completing the Residential Component receive the standalone score of Residential Assessment (Sector Insight) as a supplementary evaluation conducted in parallel with the main Real Estate Assessment.
GRESB Public Disclosure
"GRESB Public Disclosure" was launched in 2017 to assess the levels of ESG information disclosure of listed real estate companies and funds. It achieves full coverage of the major developed listed real estate indices, which resulted in assessing 858 listed entities in 2025.
GRESB Infrastructure

Launched in 2016, "GRESB Infrastructure" marked the 10th year in 2025. It is the only benchmark that provides ESG assessment on an investable fund-by-fund basis in the infrastructure sector. It consists of three assessments, namely"Fund Assessment" evaluating infrastructure funds,"Asset Assessment" benchmarking infrastructure assets and companies which such funds invest in, and "Development Asset Assessment" which was launched in 2024.
The "Fund Assessment" mainly examines how ESG issues are integrated into the investment management process of infrastructure investment funds, while the "Asset Assessment" comprehensively assesses ESG initiatives, including ESG management systems of the infrastructure companies and the operations of the assets to be invested in, performance results such as GHG emissions, and the status of ESG risk assessments and stakeholder engagement. Another feature of the "Asset Assessment" is that the score allocation takes into account the importance of individual ESG items depending on the sector and location of the asset. "Development Asset Assessment" covers funds, infrastructure companies and developers with assets in the development phase, and assesses management and performance according to the characteristics of the assets and the phase of the development, such as pre-construction or construction.
These include operators in the transportation sector, such as airports, railroads, and roads, and network-related facilities, such as data centers, along with entities that typically operate social infrastructure, such as schools and hospitals. Globally, 135 funds participated in "Fund Assessment", 653 assets in "Asset Assessment" and 17 assets in "Development Asset Assessment". From Japan, 2 assets participated in Asset Assessment.
In September 2022, the Government Pension Investment Fund (GPIF), already a member in Real Estate, became Japan's first investor member in Infrastructure as well. Further recognition is expected in the future.
These include operators in the transportation sector, such as airports, railroads, and roads, and network-related facilities, such as data centers, along with entities that typically operate social infrastructure, such as schools and hospitals. Globally, 135 funds participated in "Fund Assessment", 653 assets in "Asset Assessment" and 17 assets in "Development Asset Assessment". From Japan, 2 assets participated in Asset Assessment.
In September 2022, the Government Pension Investment Fund (GPIF), already a member in Real Estate, became Japan's first investor member in Infrastructure as well. Further recognition is expected in the future.
Contact
For further information, please email us by clicking the "Contact" at the top right of this web page.
